Table of Contents
ToggleIn the ever-evolving world of software development, microservices architecture stands out like a superhero in a sea of caped crusaders. It slices through monolithic applications with the precision of a well-sharpened knife, allowing developers to build, deploy, and scale applications faster than you can say “dependency injection.” But what truly makes this architecture shine is its diagram—a visual roadmap that transforms complex systems into digestible bites.
Overview of Microservices Architecture
Microservices architecture divides applications into smaller, independently deployable services. Each service represents a specific business function and communicates over well-defined APIs. This approach enhances scalability and allows teams to work on different components without affecting the entire application.
Scalability stands as one of the key benefits. Developers can scale individual services based on demand, which leads to efficient resource utilization. For instance, during peak usage, only the high-demand services require additional resources, optimizing overall system performance.
Deployment frequency increases along with the use of microservices. Continuous integration and continuous deployment practices simplify the update process. Teams can release new features or fixes rapidly without interfering with the entire system.
Resilience also emerges as a significant advantage. In microservices architecture, if one service fails, it does not bring down the entire application. This modularity improves fault tolerance and provides better user experience even during individual service outages.
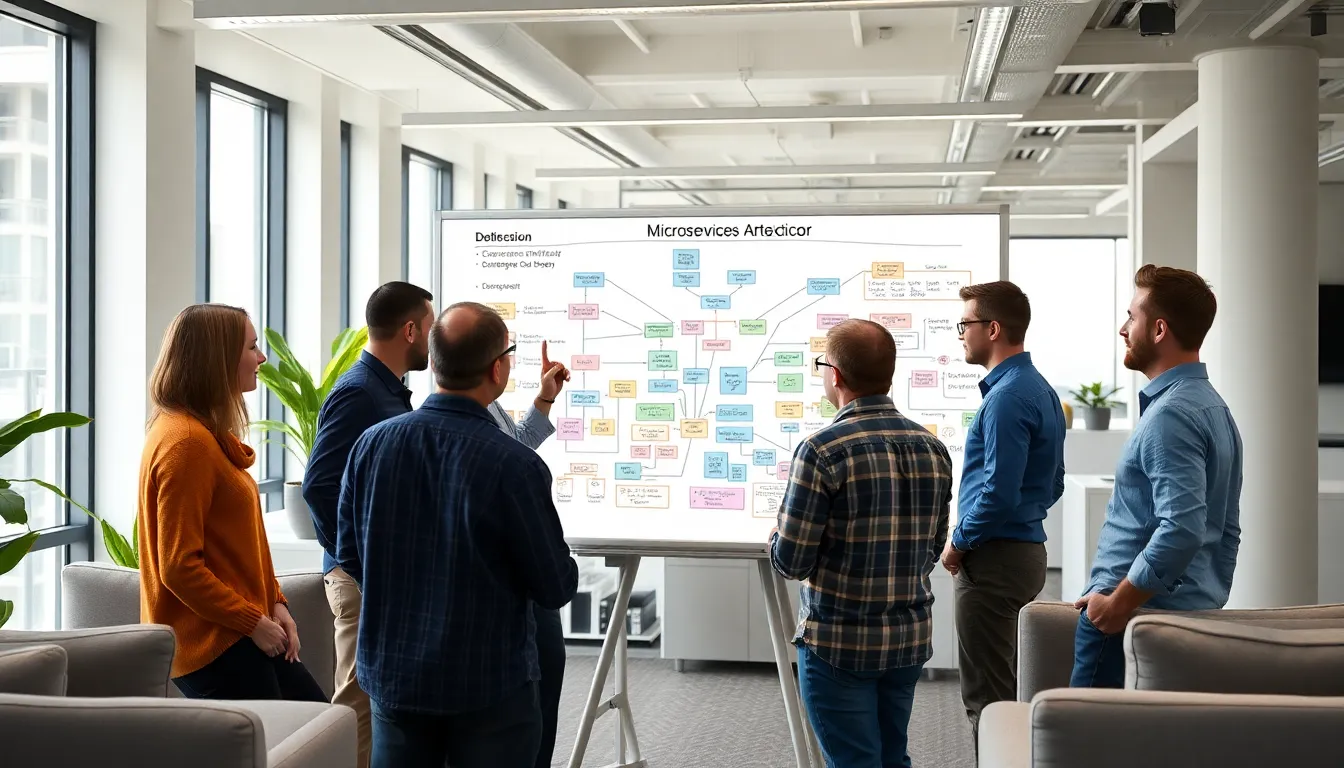
Monitoring and management benefit greatly from the diagrammatic representation of microservices. Diagrams clarify complex interdependencies among services, making it easier for developers to understand architecture and navigate issues. Visual aids become essential for maintaining clear communication within teams.
Security measures can be tailored for each service. Unique authentication and authorization protocols enhance overall system security by isolating vulnerabilities to individual services. This targeted approach decreases risk compared to traditional architectures, where a single breach can compromise the entire system.
Overall, microservices architecture fosters flexibility and innovation. Development teams gain the ability to adopt new technologies and respond quickly to market changes, which ultimately provides a significant competitive edge in today’s fast-paced digital landscape.
Key Components of Microservices Architecture
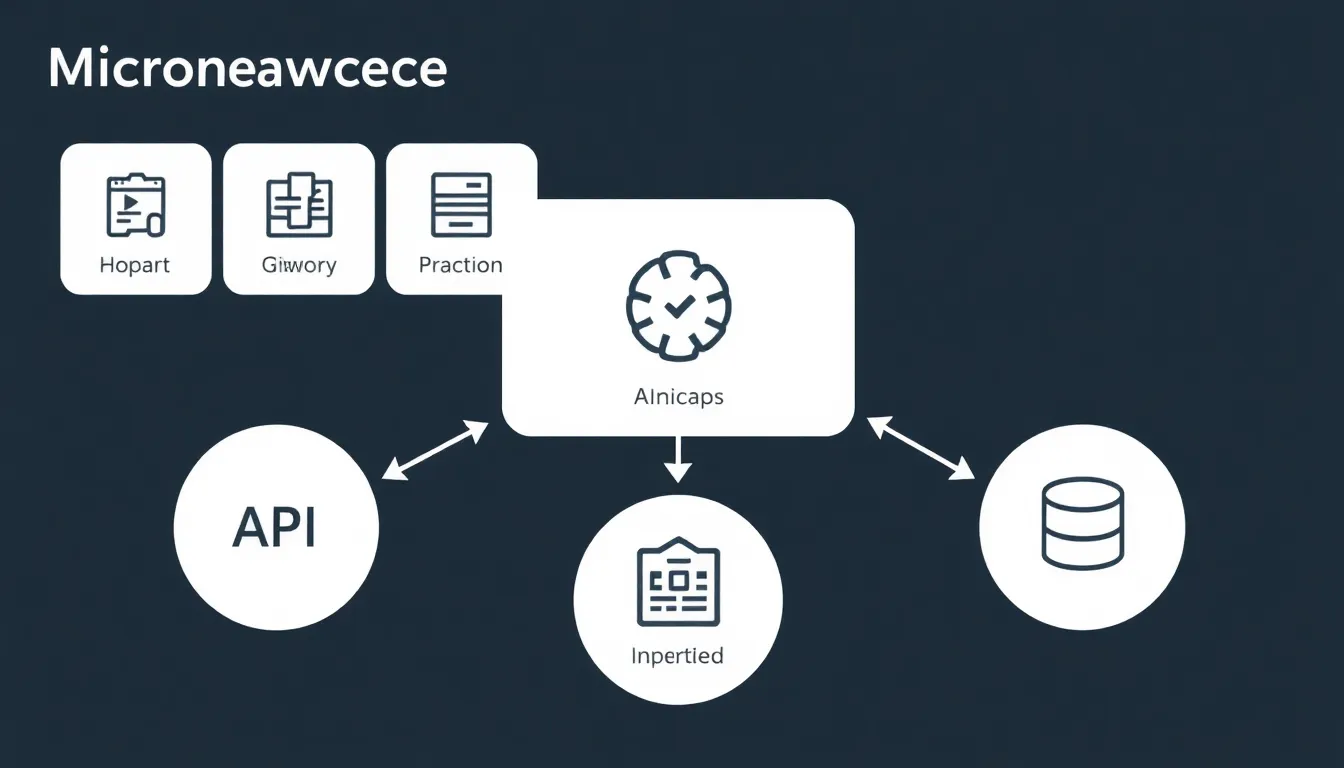
Microservices architecture relies on several key components to ensure effective operation and maintainability. Understanding these components helps in visualizing the overall structure and system dynamics.
Services
Services represent the core of a microservices architecture. Each service encapsulates a specific business function, allowing for independent deployment and scaling. Developers design services to communicate over defined APIs. Isolation enhances fault tolerance because the failure of one service does not affect others, maintaining application availability. Additionally, teams can utilize various programming languages and frameworks for different services, optimizing performance based on each service’s requirements.
API Gateway
An API gateway acts as the single entry point for client requests in a microservices architecture. It simplifies communication by routing requests to the appropriate services, managing traffic efficiently. Security features, such as authentication and authorization, can be centrally handled at the gateway level. Performance monitoring and logging capabilities help identify and resolve issues quickly. This component reduces complexity for clients, enabling them to interact with multiple services seamlessly.
Database
Databases in microservices architecture can follow various patterns. Each service can have its own database, promoting data ownership and reducing shared dependencies. This independence allows teams to select the best database technology suited for each service’s needs. Moreover, utilizing different database solutions supports flexibility in data handling and performance optimization. Developers must implement strategies for data consistency and communication between services to ensure seamless operation and reliability.
Benefits of Microservices Architecture
Microservices architecture offers significant advantages in modern software development. It enhances scalability and flexibility for development teams, making it easier to manage complex applications.
Scalability
Scalability stands out as a primary benefit of microservices architecture. Individual services can scale based on demand without affecting the entire application. Developers prioritize resources where needed, optimizing performance during peak usage. This model supports horizontal scaling, allowing for additional instances of any service to improve overall capacity. Businesses can respond to user needs quickly, preventing performance bottlenecks. By dynamically adjusting resources, teams ensure applications remain responsive and efficient.
Flexibility
Flexibility is another crucial advantage of this architecture. It allows teams to adopt new technologies and tools with minimal disruption. Development teams can choose the best frameworks or languages for specific services, fostering innovation. Since each service operates independently, changes can occur without coordinating with the entire application. This capability encourages rapid experimentation and iteration, enabling faster feature launches. Additionally, it helps organizations stay competitive in the market by quickly responding to changes and user feedback.
Creating a Microservices Architecture Diagram
Creating a microservices architecture diagram simplifies the visualization of complex interactions among services. This diagram serves as a vital tool for understanding the system’s structure and dependencies.
Steps to Create the Diagram
Identify key services that make up the application, defining their specific business functions. Map out communication pathways between these services, ensuring to clarify the APIs used for interaction. Select an appropriate database system for each service, emphasizing data ownership and reducing dependencies. Include an API gateway to streamline requests from clients, enhancing security and traffic management. Document any external dependencies or integrations that may affect service performance or reliability.
Tools for Diagram Creation
Utilize software tools like Lucidchart or Draw.io for their intuitive interfaces and collaborative features. MindMeister also offers options for mapping services visually. Include PlantUML for code-based diagramming, providing flexibility in design changes. Miro caters to teams seeking a more interactive approach. Consider tools like Microsoft Visio for in-depth design capabilities, benefiting larger projects that require comprehensive diagrams.
Best Practices for Microservices Architecture
Designing microservices architecture requires specific best practices to enhance performance and maintainability.
- Decouple Services: Each service must function independently, allowing teams to deploy and scale without affecting others. This independence decreases the chance of failures during deployments and increases overall system reliability.
- Implement Smart Routing: Utilize an API gateway for intelligent routing of requests. A well-structured API gateway serves as the single entry point and manages traffic, providing security features.
- Automate Testing: Continuous integration and testing practices ensure code quality. Automated testing prevents issues from reaching production, allowing teams to identify and fix defects promptly.
- Monitor Performance: Employ monitoring tools to track service performance and health. Observability into service interactions supports proactive maintenance and quick response to potential problems.
- Adopt DevOps Practices: Foster collaboration between development and operations teams. DevOps practices enhance communication and streamline the deployment process, ensuring faster delivery of features.
- Manage Data Strategically: Data ownership should reside with individual services. Decentralized database management allows services to utilize the best technology for their requirements and promotes efficient data access.
- Ensure Robust Security: Implement security measures specific to each service. Tailored security protocols reduce vulnerabilities and protect sensitive data effectively.
- Focus on Continuous Improvement: Encourage a culture of learning and adaptation. Continuous feedback loops enable teams to refine processes and improve the microservices ecosystem consistently.
Applying these best practices optimizes microservices architecture, enhancing scalability, flexibility, and resilience while ensuring effective collaboration within development teams.
Microservices architecture represents a transformative approach to software development that enhances scalability and flexibility. By breaking applications into smaller, independent services, teams can innovate rapidly and respond to market demands more effectively.
The use of diagrams not only simplifies the understanding of complex systems but also aids in managing interdependencies and ensuring robust security. Adopting best practices in microservices design further optimizes performance and maintainability, setting organizations up for long-term success in a competitive landscape.
As businesses continue to evolve, embracing microservices architecture will be vital for fostering innovation and achieving operational excellence.





